Disclosure regarding our editorial content standards.
In August 2020, the average interest rate for a two-year personal loan was 9.34 percent, according to the Federal Reserve. Interest rates for personal loans can run anywhere from 10 percent to a little over 30 percent, depending on your credit score, financial health, debt, annual income and the current state of the market.
Personal loan rates can drop below 10 percent, however, if you use an online lender or take out an unsecured loan. These types of loans can offer quick solutions to unexpected financial hardship, from a sudden medical bill to needing a home remodel.
We break down what you need to know to get yourself in the best position to apply for a loan, get an interest rate that you can handle over the long term and tips on making sure you’re well-suited for a loan.
What is a good interest rate for a personal loan?
A good interest rate for a personal loan is one that’s below the national average, which is 9.41 percent according to recent Experian data.
The rate you’re offered is dependent on a variety of factors, including your credit score, debt-to-income ratio and more. These affect the loan interest rate and other terms you can expect to receive when applying—but more on that later.
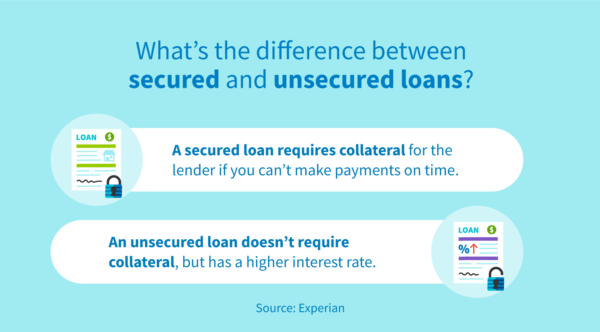
How to apply for a personal loan
Before you fill out your personal loan application, it’s a good idea to check both your credit score and credit report so you can see what lenders will be looking at when they perform a credit check. This includes looking at any derogatory marks or other factors that may stand in the way of you getting approved.
As a reminder, you can request a free credit report from the three major credit bureaus throughout the year, and checking on your credit score does not bring it down. It’s also advised to determine how much you need to borrow as well as your ideal interest rate.
If you want to shop around for the best lender, you may want to consider applying for pre-approval. This is a great way to compare multiple quotes without pulling a full credit report, which can affect your score. From there, you can apply to the lender of your choosing based on your ideal rate.
Once you’ve taken any necessary steps to get your credit in good standing, you can apply for a personal loan through a financial institution—this includes banks, credit unions and online lenders. You’ll need to fill out an online application and provide your Social Security number so the lender can check your credit history. Remember that every lender you apply through will check your credit report and score, if you choose to apply before getting pre-approved.
Lenders will usually heavily weigh your credit score when determining whether or not you’re approved—and a higher score will usually unlock better interest rates and loan terms. This is why determining your score ahead of time is important to see if you could be qualified for better rates and loan terms on any loans you apply for.
How do personal loan interest rates stack up to other loan types?
Getting a car, buying a home, going back to school or starting your own business are among the most common reasons to take out a loan. These circumstances, among others, all warrant taking out a loan, and loan interest rates can vary widely by category based on these circumstances.
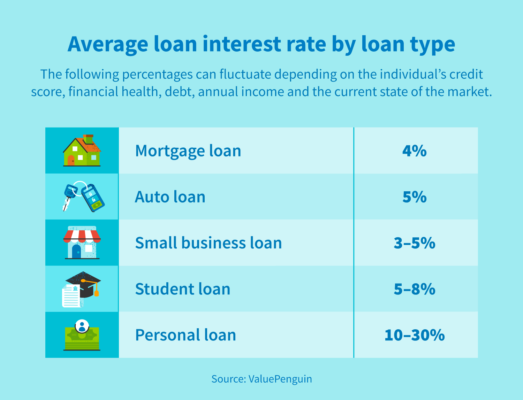
If you need a loan for any of these reasons, or another one that’s not listed, you’ll be looking at an interest rate anywhere from 3 to 200 percent on the amount you want to borrow. The exact interest rate depends on the lender you choose, the length of your loan and a variety of other factors (including your credit score).
To give you a better idea of what to expect when applying for a loan, we’ve outlined the most common loans and their average interest rates so you can plan ahead with peace of mind.
Average auto loan interest rates
The average auto loan interest rate is around 5 percent for a five-year loan—specifically, the Federal Reserve lists the average rate on a 48- or 60-month new car loan as 4.98%. However, this percentage can skyrocket to 15 percent if your credit score is 600 or lower. Interest rates are lower across the board for used cars—so if you have an average or poor credit score, it’s recommended to buy something used (or lease, in some circumstances) to avoid unnecessarily high interest rates and work on building your credit score up over time.
Average mortgage loan interest rates
A good mortgage loan interest rate is 4 percent or lower, but rates can vary. While the most common loans for buying a new home are for 15 or 30 years with fixed rates, there are other options available for veterans and those in lower-income brackets.
Specifically, Freddie Mac lists mortgage rates as follows as of December 2020:
- 30-year fixed rate mortgage: 2.7 percent
- 15-year fixed rate mortgage: 2.3 percent
- 5/1-year adjustable rate mortgage: 2.8 percen
Average student loan interest rate
Student loans are a bit different than the auto and mortgage loans above. When it comes to federal student loans, the government sets a nationwide interest rate. Typically, these rates fall between 5 and around 8 percent and can change depending on the type of loan, who is borrowing and whether you’re attending a private or public school. According to the Office of Federal Student Aid, interest rates are as follows for student loan borrowers:
- Undergraduate borrowers: 2.75 percent for both direct subsidized and unsubsidized loans
- Graduate or professional borrowers: 4.30 percent for direct unsubsidized loans
- Parents, graduate or professional borrowers: 5.30 percent for direct PLUS loans
There are private loan options available for students as well, but they require payments earlier than most federal student loans. Private lenders also take into account the student’s credit score, unlike federal lenders, which can further increase your interest rate unless you have a cosigner with a long credit history.
Small business loan interest rates
Typically, small business owners can expect to pay 3 to around 5 percent in interest when they take out a loan. These rates can vary significantly depending on the lender (banks tend to offer a lower rate than online lenders, for example) and the loan amount.
If you do choose to go with an online lender, or if you’re looking for a line of credit or a cash advance, your loan interest rate can hit up to 200 percent.
How your credit score affects loan rates
Your credit score is an indication to banks and online lenders how much of a risk they’re taking in loaning to you. If you have a long history of being an active credit card user and paying your bills on time, you’re generally seen as less of a risk and can receive a lower interest rate.
Credit scores can range from 300 to 850. A score of 650 or above is typically considered to be a good credit score, although what is considered good can vary by bank, lender and credit scoring model. Excellent credit scores fall within the 750 to 850 range and can significantly increase your lender’s confidence in your ability to pay them back. This can ultimately score you a lower interest rate.
Bad credit scores of 500 and lower can sometimes disqualify you from receiving a loan at all, or send your interest rates up dramatically, meaning you may want to work to increase your credit score before applying for a loan of any kind.
What else affects my loan interest rate?
While the type of loan and your credit score are significant factors for your average interest rate, there are other considerations lenders and credit unions account for when calculating your rate. Some of those additional factors include:
- Your credit history. This includes the amount of time you’ve had lines of credit open, your payment history, late payments and hard inquiries you’ve had over recent years.
- Annual income and employment history. Lenders want to know that you’re in a secure place financially to take on a loan, so they often request proof of annual income to make sure you meet their requirements. Your job industry can also come into effect here, as stability and profitability can improve their confidence in you.
- Loan size and length. While some loans have a timeline generally agreed upon by lenders and borrowers (like a 15- or 30-year mortgage loan or 60-month auto loan) others vary entirely based on borrower’s needs. If you choose a longer loan term, you could end up paying up to 2 percent more in interest than if you stay with traditional loan lengths.
- Type of loan and lender. The type of loan you need and the lender you choose will impact your interest rate. This is why shopping around is your best bet for securing the best interest rate.
- Debt-to-income ratio. Another factor lenders look into when calculating your interest rate is the amount of debt you have incurred relative to your income. This includes credit card debt and other loans you have yet to pay off. Generally, in our experience, lenders are looking for a 35–45 DTI ratio, which is one more reason to aim to keep your DTI ratio low.

Difference between fixed and variable loan interest rates
A fixed loan interest rate simply means that the amount of interest you’re required to pay stays static over your entire loan, which keeps payments the same and avoids any surprises down the line. Fixed rates are recommended for long-term loans, including a mortgage or auto loan.
A variable loan interest rate, also known as a floating loan interest rate, is a type of loan with a rate that can fluctuate over time, depending on the market. This option is a bit riskier, but the rates tend to be lower to start with, making it a good choice for short-term loans that will get paid back quickly.
Loans, while seemingly complicated, are pretty standard across lenders. Fixing your credit if needed and taking stock of your credit history are key components to finding the best deal possible to ensure that you don’t walk away with a high annual percentage rate.






